Muscles of the Arm
Origin, Insertion & Innervation
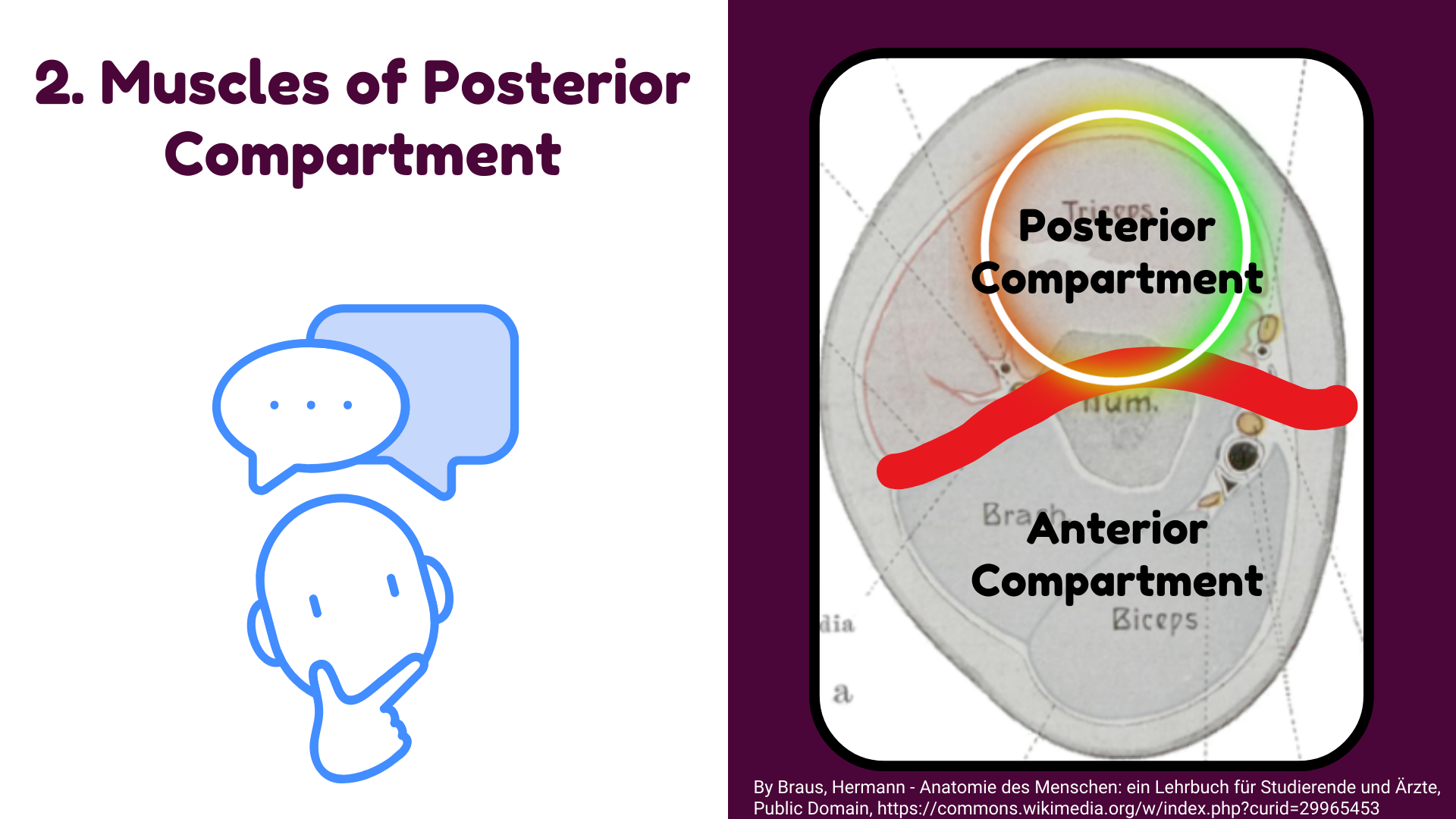
Division of Arm
The arm is divided by the deep fascia into
Anterior and Posterior compartments.
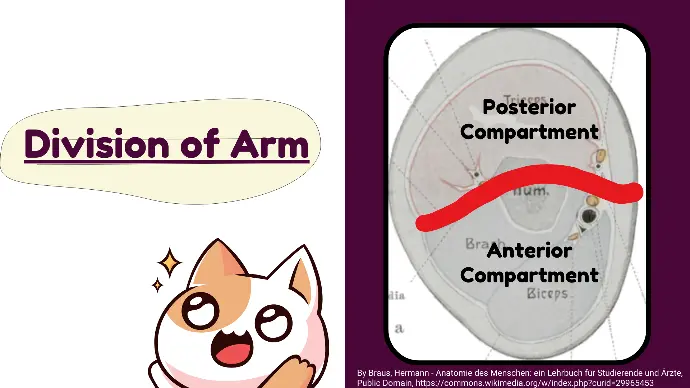
- Anterior compartment contains the Flexor muscles.
- Posterior compartment contains the Extensor muscles.
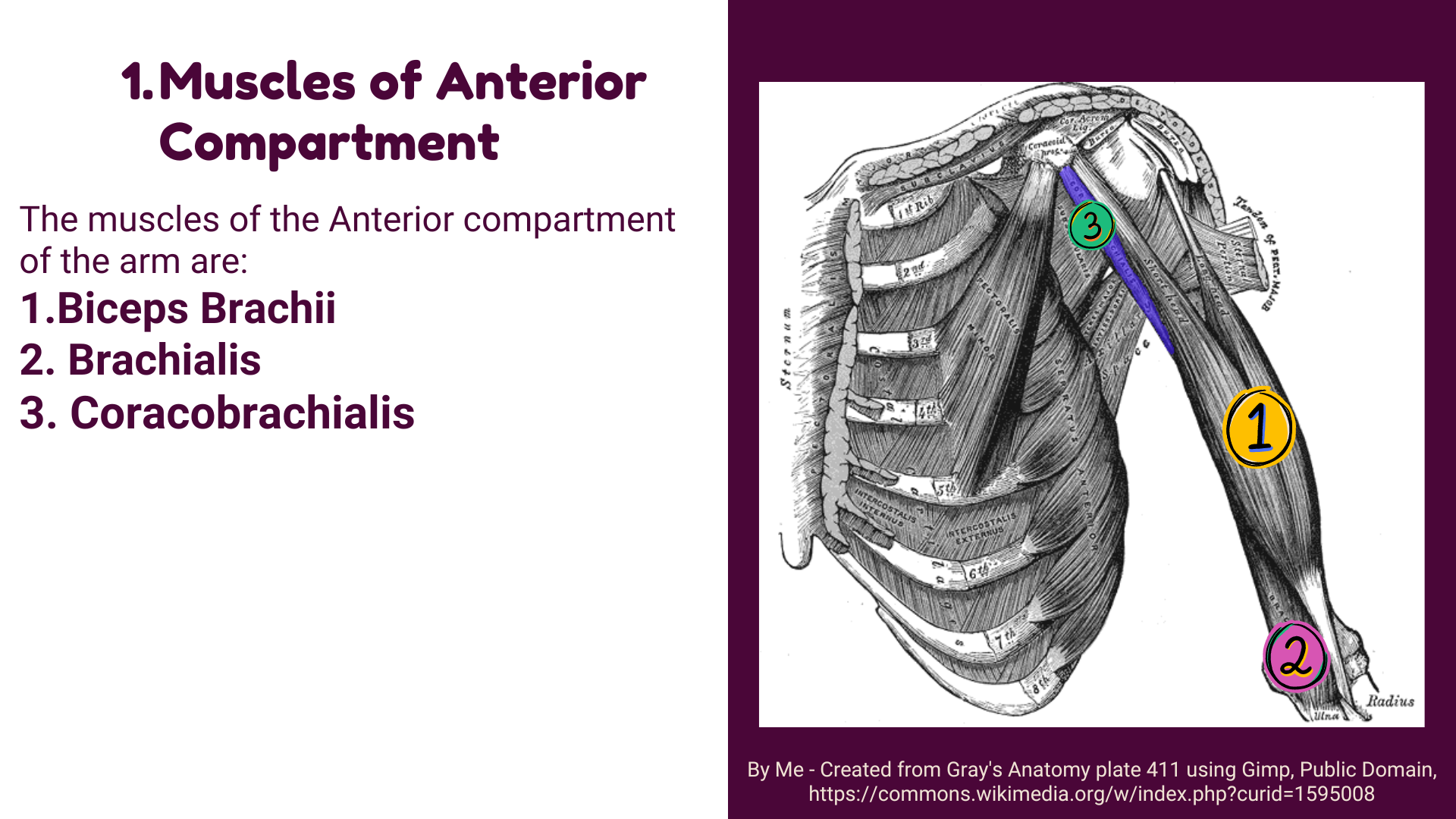
Muscles of Anterior Compartment
The muscles of the Anterior compartment of the arm are:
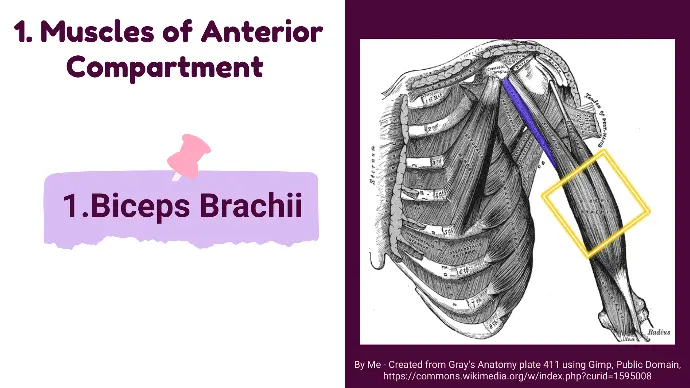
1.Biceps Brachii
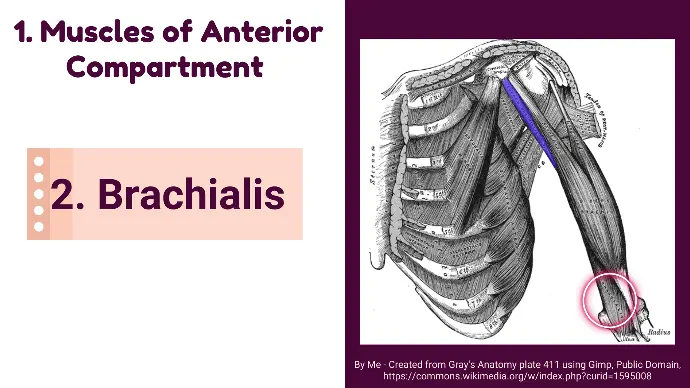
2. Brachialis
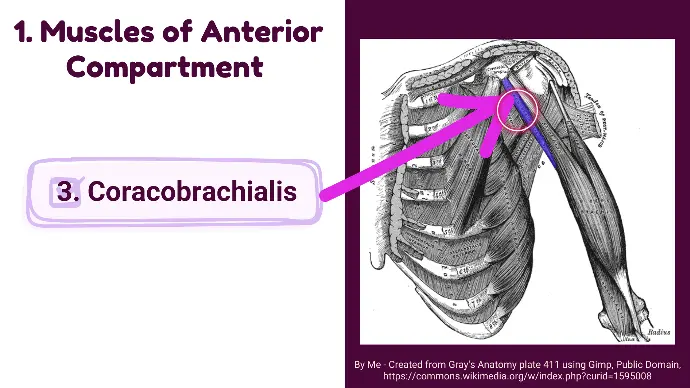
3. Coracobrachialis
1. Biceps Brachii
It lies superficial in the anterior compartment, crossing the shoulder and elbow joints.
- Origin:
Long Head: Supraglenoid tubercle of the scapula.
Short Head: Coracoid process of the scapula.
- Insertion: Radial tuberosity and bicipital aponeurosis.
- Innervation: Musculocutaneous nerve (C5, C6).
2. Brachialis
It is positioned deep to the biceps brachii.
- Origin: Lower half of the anterior surface of the humerus.
- Insertion: Coronoid process and tuberosity of the ulna.
- Innervation: Musculocutaneous nerve (C5, C6) and radial nerve (C7).
3. Brachialis
It is located medially, assisting in shoulder flexion and adduction.
- Origin: Coracoid process of the scapula.
- Insertion: Medial surface of the humerus at the level of the deltoid tuberosity.
- Innervation: Musculocutaneous nerve (C5, C6, C7).
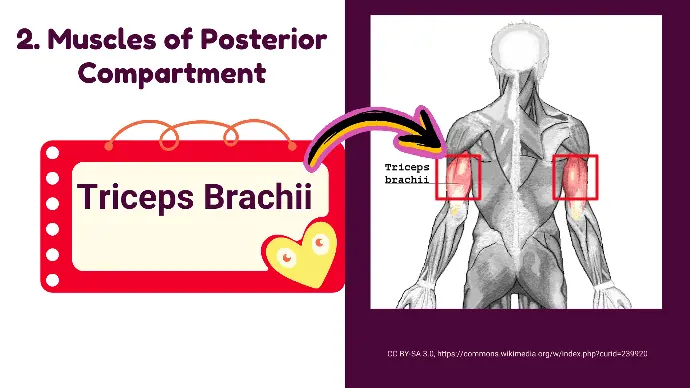
Muscles of Posterior Compartment
The Posterior Compartment has only One muscle:
Triceps Brachii Muscle
Triceps Brachii Muscle
It is the only muscle in the posterior compartment, providing powerful extension of the elbow.
Origin:
- Long Head: Infraglenoid tubercle of the scapula.
- Lateral Head: Posterior surface of the humerus, above the radial groove.
- Medial Head: Posterior surface of the humerus, below the radial groove.
Insertion: Olecranon process of the ulna.
Innervation: Radial nerve (C6, C7, C8).