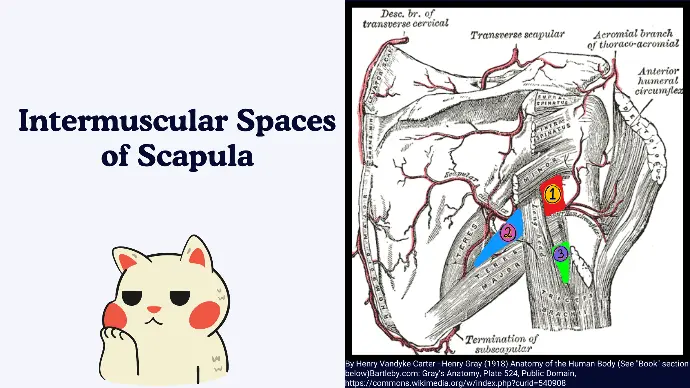
Intermuscular Spaces of Scapula
The scapula contains three important spaces, that are formed due to the specific attachments of its muscles.
They are clinically significant due to the neurovascular structures they transmit.
Intermuscular Spaces of Scapula
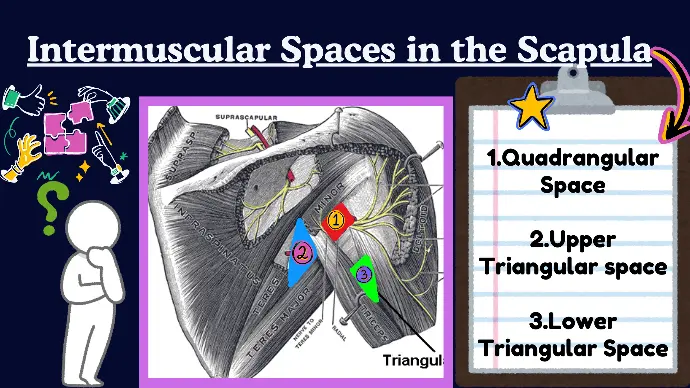
There are Three intermuscular spaces of Scapula:
- Quadrangular Space
- Upper Triangular space
- Lower Triangular Space
1. Quadrangular Space
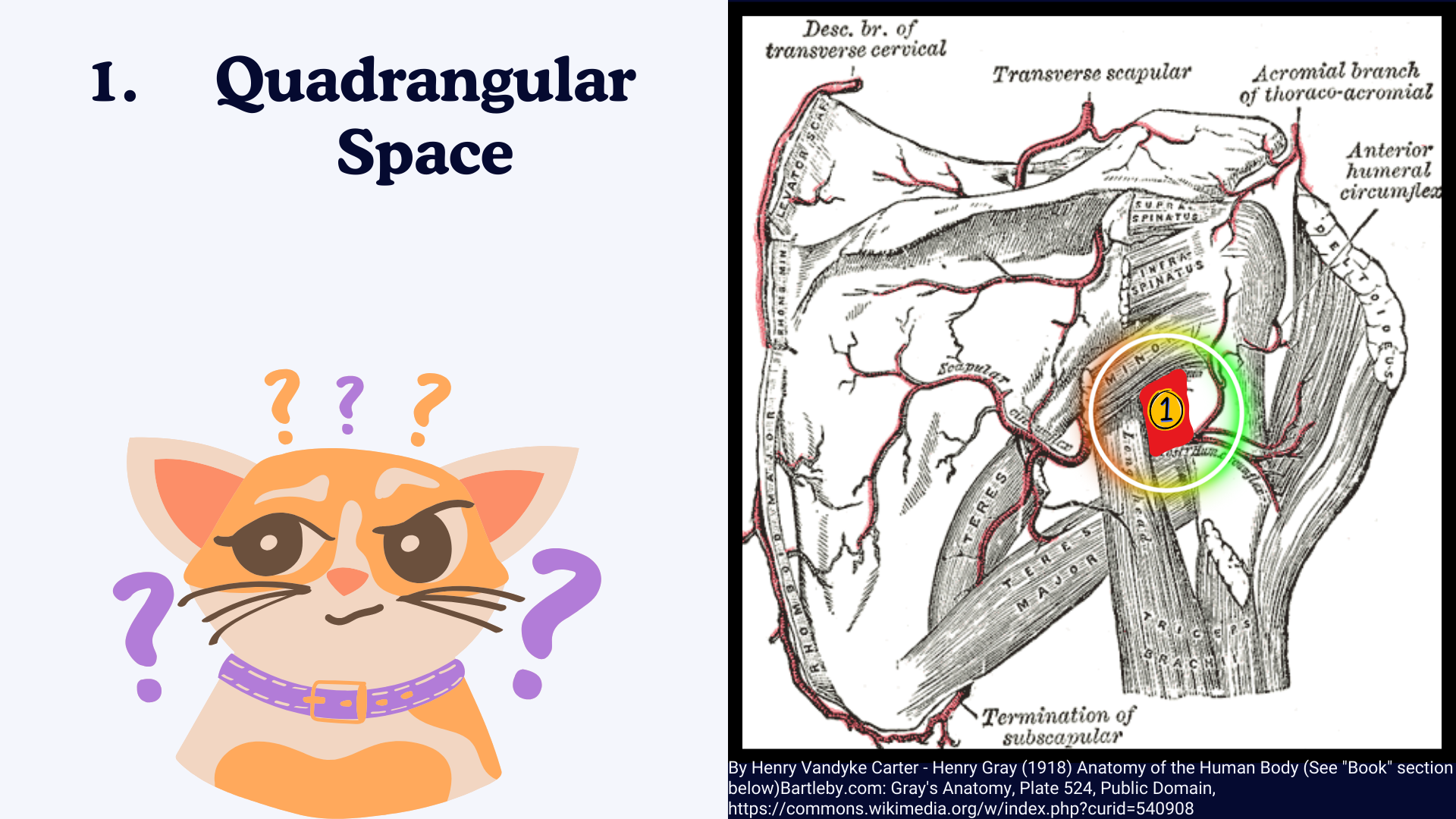
Boundaries of Quadrangular Space:
Since it has 4 sides, so it has 4 boundaries.
- Superior: Teres minor.
- Inferior: Teres major.
- Medial: Long head of the triceps brachii.
- Lateral: Surgical neck of the humerus.
Contents of Quadrangular Space:
- Axillary Nerve: Innervates the deltoid and teres minor muscles.
- Posterior Circumflex Humeral Artery: Supplies blood to the deltoid and shoulder joint.
Clinical Significance of Quadrangular Space:
Quadrangular Space Syndrome:
It is the Compression of the axillary nerve or posterior circumflex humeral artery leading to shoulder pain, weakness, and possible deltoid muscle atrophy.
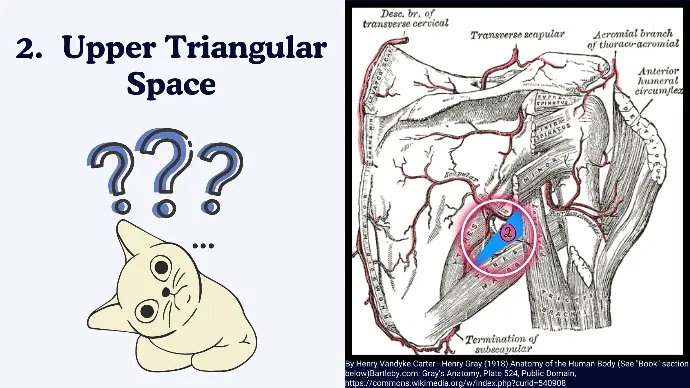
2. Upper Triangular Space
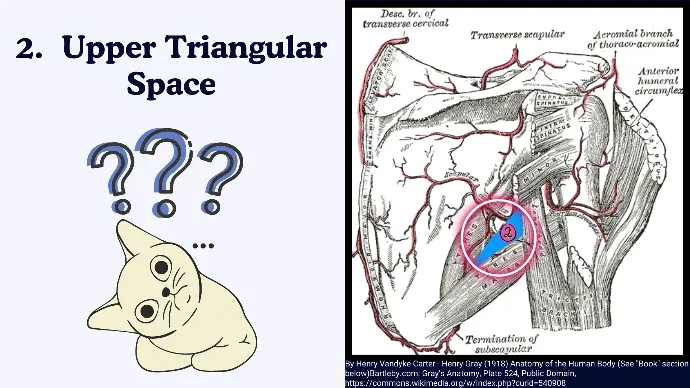
Boundaries of Upper Triangular Space:
Since a Triangle has 3 sides, so it has 3 Boundaries.
- Superior: Teres minor.
- Inferior: Teres major.
- Lateral: Long head of the triceps brachii.
Contents of Upper Triangular Space:
- Circumflex Scapular Artery: A branch of the subscapular artery that supplies the scapular region.
Clinical Significance of Upper Triangular Space:
The triangular space is less commonly associated with clinical conditions but is important for its vascular supply to the scapular region.
3. Lower Triangular Space
Boundaries of Lower Triangular Space:
Since a triangle has 3 sides, so it has 3 Boundaries.
- Superior: Teres major.
- Medial: Long head of the triceps brachii.
- Lateral: Shaft of the humerus.
Contents of Lower Triangular Space:
- Radial Nerve: Innervates the posterior compartment of the arm and forearm.
- Profunda Brachii Artery (Deep Brachial Artery): Supplies blood to the posterior compartment of the arm.
Clinical Significance of Lower Triangular Space:
- Radial Nerve Compression: Can lead to radial nerve palsy, resulting in wrist drop and sensory deficits in the posterior arm and hand.
- Fractures of the Humerus: The radial nerve is at risk of injury in midshaft humeral fractures, often involving the triangular interval.
Anatomical Relationships of Intermuscular Spaces of Scapula:
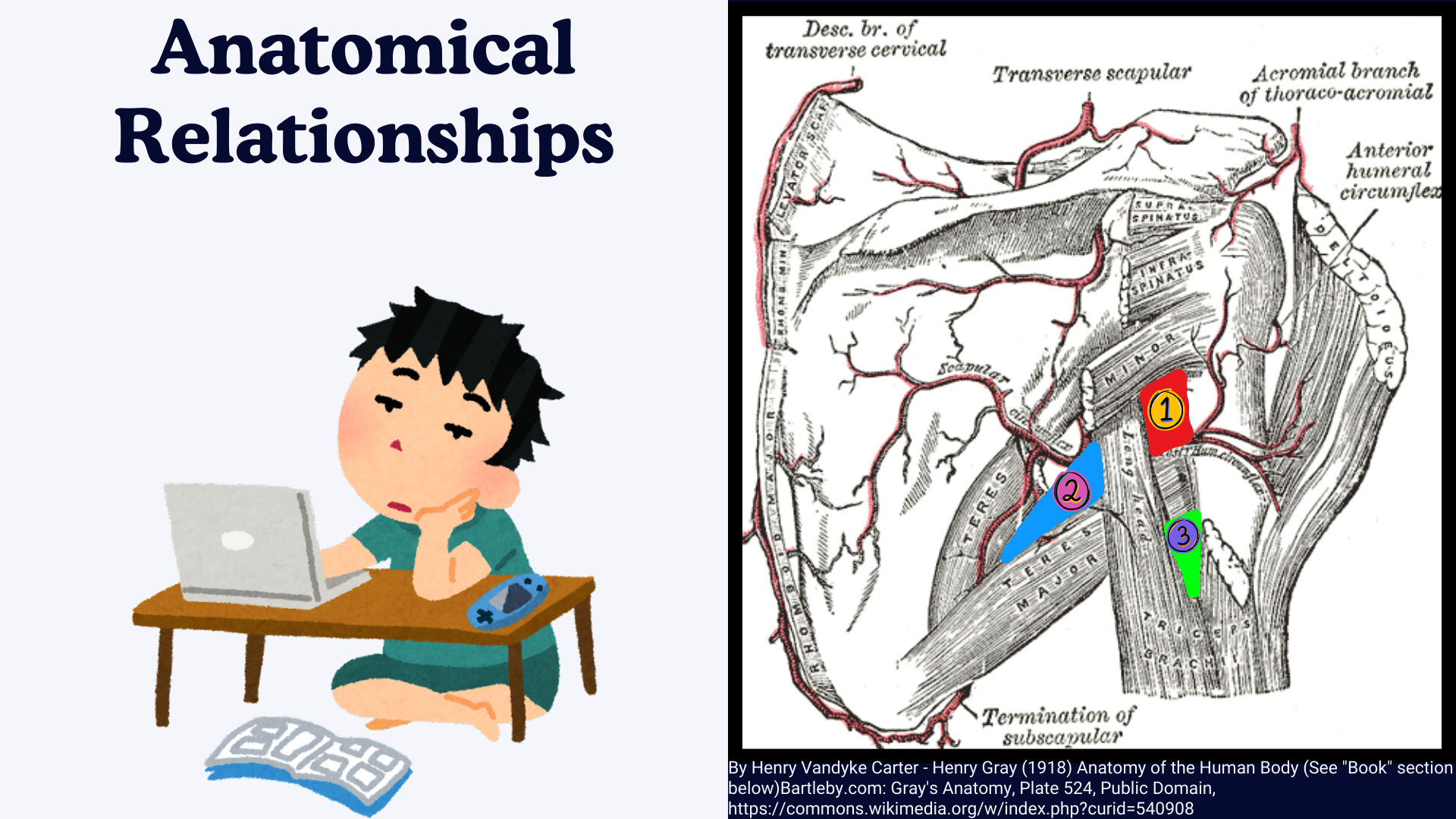
- Muscular Relationships: The spaces are defined by important shoulder muscles, including the teres major, teres minor, and the long head of the triceps brachii.
- Vascular Relationships: The spaces transmit key arteries that supply the shoulder and upper arm regions.
- Nervous Relationships: The spaces contain important nerves, such as the axillary nerve and radial nerve, which are crucial for the motor and sensory innervation of the upper limb.