HIV virus
Structure and Routes of Transmission

What is HIV virus?
HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) is a retrovirus belonging to the Lentivirus subgroup. This group is characterized by causing slow-progressing infections with long incubation periods. HIV is a human T-cell lymphotropic virus, meaning it primarily targets T cells in the immune system.
Types of HIV virus
There are two main types of HIV:
- HIV-1: The most common type globally.
- HIV-2: Primarily found in West Africa and is less aggressive compared to HIV-1.
RNA of HIV
HIV is a positive single-stranded RNA virus with a diploid RNA, meaning it has two identical RNA molecules.
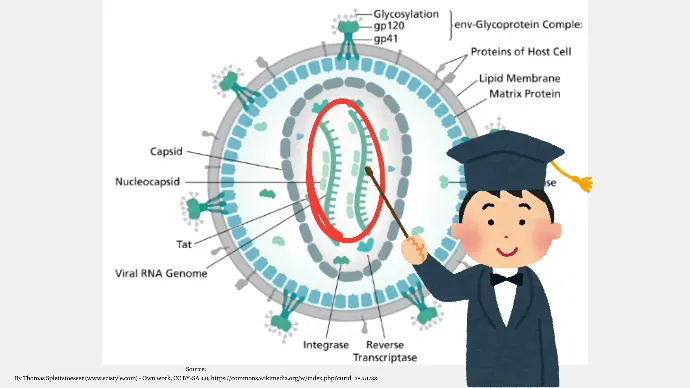
Structure of HIV
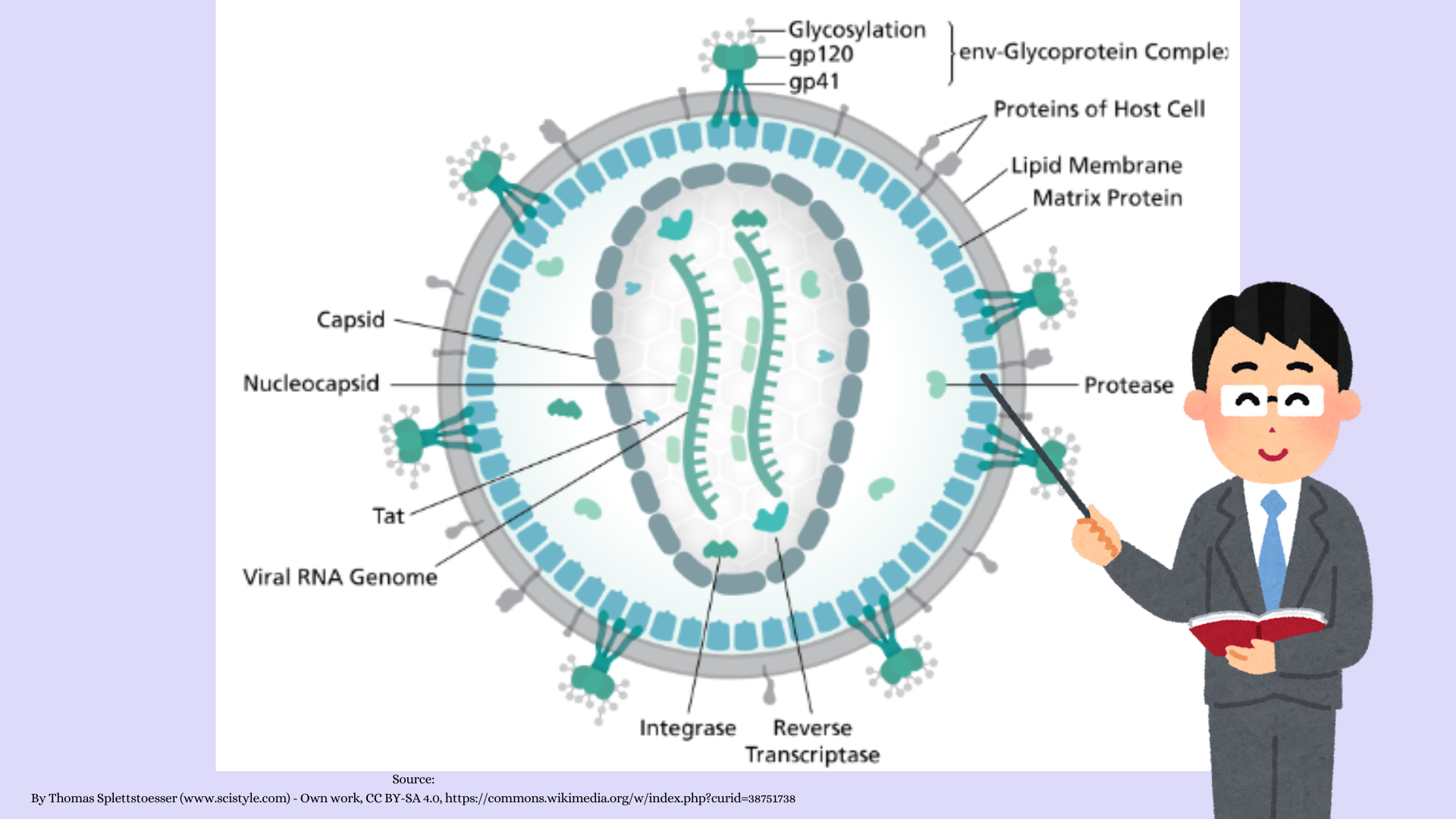
- Core: HIV has a cylinder-shaped core (Type D) that houses its genetic material and enzymes.
- Enzymes: The core contains essential enzymes like reverse transcriptase, integrase, and protease.
- Envelope: Surrounding the core is an envelope embedded with viral-specific glycoproteins (gp120 and gp41).
- Genome: The genome is composed of two single-stranded RNA molecules of positive polarity.
Enzymes of HIV
It has 3 special enzymes:
- Reverse transcriptase
- Integrase
- Protease
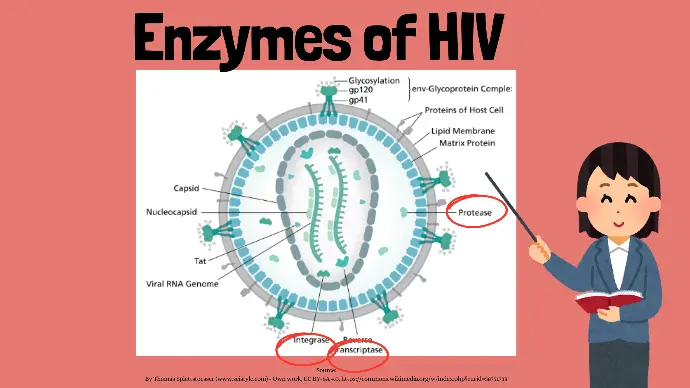
HIV relies on these three critical enzymes for its life cycle:
- Reverse Transcriptase: Converts viral RNA into DNA.
- Integrase: Integrates viral DNA into the host's genome.
- Protease: Cleaves newly synthesized polyproteins to create mature viral proteins.
Targets of HIV virus
Through gp120 on its envelope, HIV virus attaches to two targets on cell surface before fusion.
- INITIAL TARGET:
CD4 receptor
(this receptor is found on helper T cells , mononuclear cells and macrophages.
- Second targets ( chemokine receptors):
- CCR5 receptors (macrophages)
- CXCR4 receptors ( Helper T cells)
MODE OF TRANSMISSION of HIV virus
There are 4 Modes of Transmission of HIV.
- SEXUAL Transmission (Homosexual, Heterosexual, Oral)
- PARENTERAL Transmission: Through blood and blood products.
- VERTICAL Transmission ( During pregnancy, During childbirth)
- It also passes via Breast feeding the baby.
