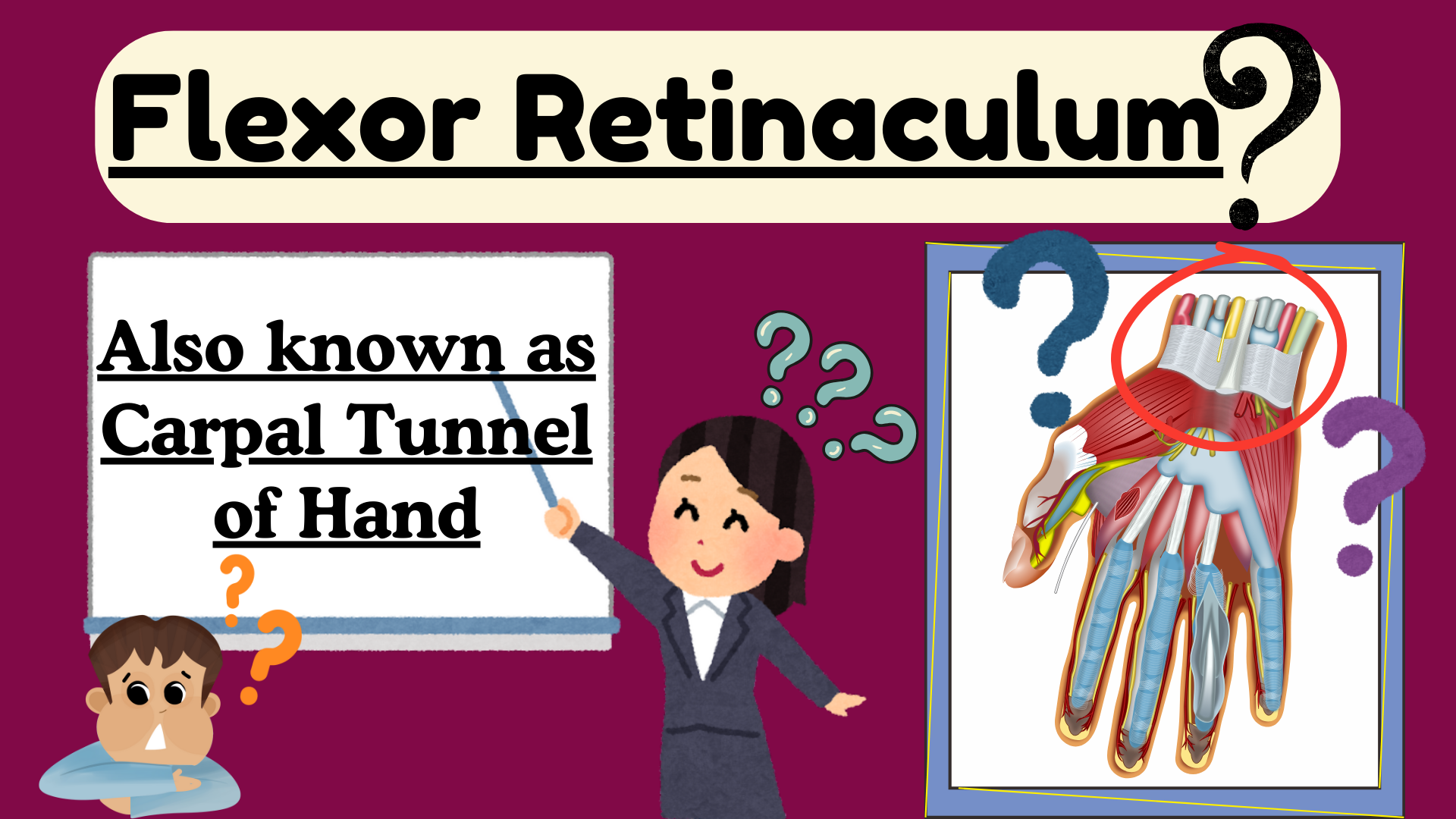
Flexor Retinaculum of Hand
Anatomy of Carpal Tunnel of Hand
The flexor retinaculum is a strong, fibrous band located on the palmar side of the wrist.
Its primary function is to hold the flexor tendons in place as they pass through the carpal tunnel.
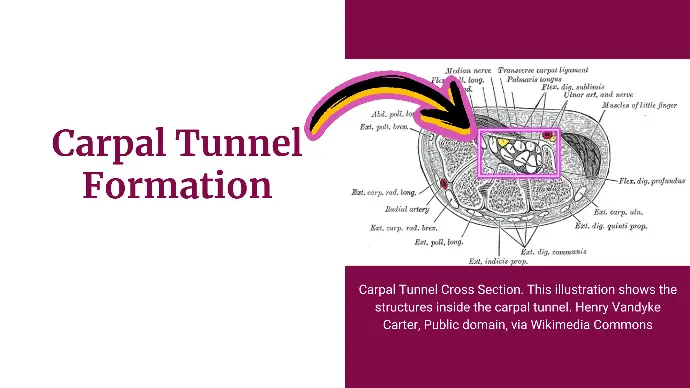
Carpal Tunnel Formation
Flexor retinaculum bridges the palmar concavity of the wrist and converts it into a tunnel, called the carpal tunnel.
Anatomy of Flexor Retinaculum
Attachments:
- Medially: Attached to the scaphoid and trapezium bones.
- Laterally: Attached to the pisiform and hook of the hamate bones.
Tunnels within Carpal Tunnel
Besides forming the Main Carpal Tunnel, Flexor retinaculum also forms 2 extra smaller tunnels within it.
These tunnels are called Slips.
They allow specific structures to pass through them.
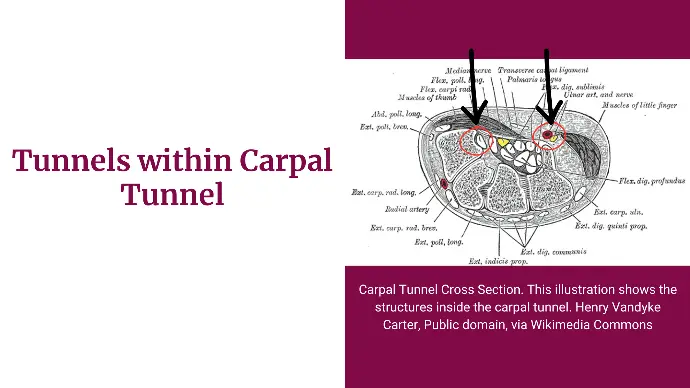
These are:
- Lateral Deep Slip: it is a tunnel for the tendon of Flexor Carpi Radialis.
- Medial Superficial Slip: Ulnar vessels and nerves pass through this tunnel.
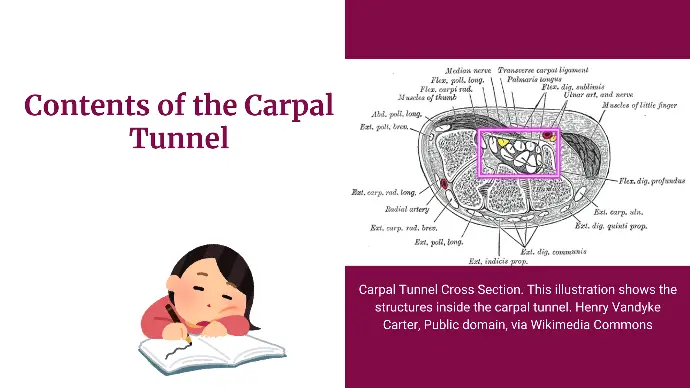
Contents of Carpal Tunnel
The flexor retinaculum forms the roof of the carpal tunnel, which contains:
- Flexor Tendons: Flexor digitorum superficialis, flexor digitorum profundus, and flexor pollicis longus tendons.
- Median Nerve: Passes through the carpal tunnel along with the flexor tendons.
Anatomical Relationships of Carpal Tunnel
Superficial Structures:
Following Structure pass superficial to Flexor Retinaculum.
- The palmar cutaneous branch of the median nerve.
- The palmar cutaneous branch of ulnar nerve.
- Ulnar nerve.
- Ulnar vessels.
- The tendon of Palmaris Longus.
- Thenar and hypothenar muscles arise from the retinaculum.
Deep Structures:
Following structure pass deep to the retinaculum.
- The carpal bones form the floor of the carpal tunnel beneath the flexor retinaculum.
- Median Nerve.
- 4 tendons of flexor digitorum superficialis.
- 4 tendons of flexor digitorum profundus.
- Radial bursa.
- Ulnar bursa.
- Tendon of flexor pollicis longus.
- Tendon of flexor carpi radialis.