Elbow Joint
The elbow joint is a hinge type of synovial joint.
it connects the lower end of Humerus to the upper ends of Radius and Ulna bones.

Anatomy of the Elbow Joint

Following points will be discussed in the anatomy of elbow joint.
- Articular surfaces
- Articulations
- Joint Capsule
- Synovial Membrane
- Ligaments of elbow joint
- Muscles of elbow joint
- Nerve Supply
- Blood Supply
1. Articular Surfaces
Following surfaces attach to form the Elbow joint.
- Superiorly: The trochlea and capitulum of humerus.
- Inferiorly:
- Head of Radius articulates with Capitulum of humerus.
- Trochlear notch of Ulna articulates with Trochlea of humerus.
2. Articulations
Three articulations are involved in Elbow joint. These are also known as
Cubital Articulations.
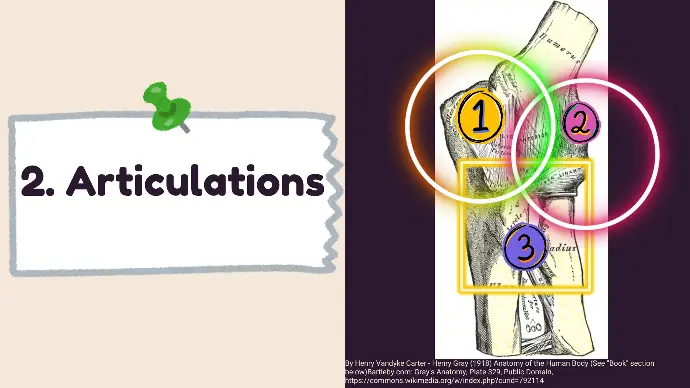
- Humeroulnar Joint: Between the trochlea of the humerus and the trochlear notch of the ulna.
- Humeroradial Joint: Between the capitulum of the humerus and the head of the radius.
- Proximal Radioulnar Joint: Between the head of the radius and the radial notch of the ulna, allowing for pronation and supination.
3. Joint Capsule
The joint capsule surrounds the elbow joint.
It provides stability while allowing movement.

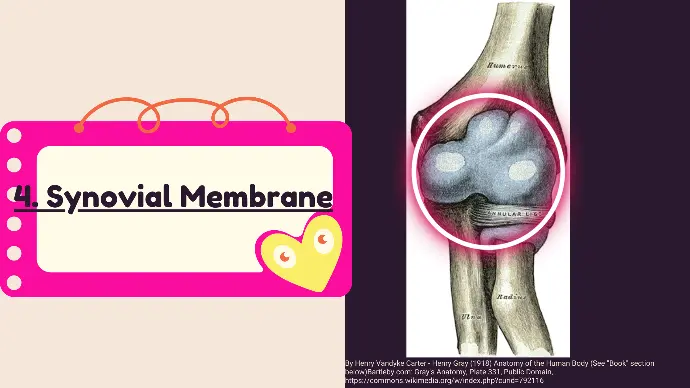
4. Synovial Membrane
It is the inner lining of the joint capsule, that secretes synovial fluid to lubricate the joint.
5. Ligaments of elbow joint
The Elbow Joint has 3 Types of Ligaments:
1. Ulnar Collateral Ligament
2. Radial Collateral Ligament
3. Anterior Ligament and Posterior Ligament
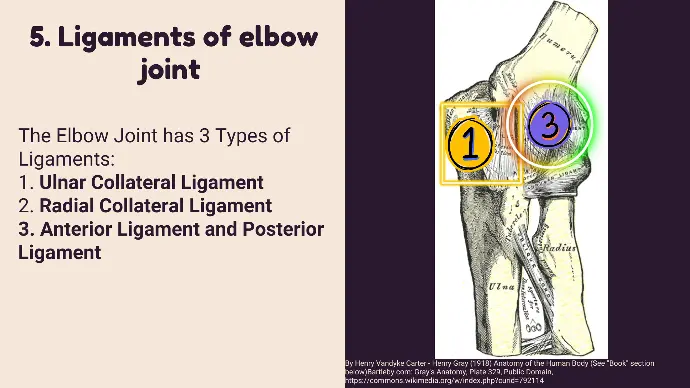
1. Ulnar Collateral Ligament
- It is also known as Medial Collateral Ligament.
- It has three bands: Anterior band, Posterior band, Oblique band.
- This ligament is crossed by Ulnar nerve.
2. Radial Collateral Ligament
It is also known as Lateral Collateral Ligament.
3. Anterior Ligament and Posterior Ligament:
These are Thickenings of the Capsule.
6. Muscles of elbow joint
Following Categories of Muscles supply the elbow joint.
- Flexor muscles
- Extensor muscles
- Pronator muscles
- Supinator muscles
1. Flexor Muscles
- Biceps Brachii: Flexes the elbow and supinates the forearm.
- Brachialis: Primary flexor of the elbow.
- Brachioradialis: Flexes the elbow, especially in a mid-prone position.
2. Extensor Muscles
- Triceps Brachii: Primary extensor of the elbow.
- Anconeus: Assists in elbow extension and stabilizes the joint.
3. Pronator Muscles
- Pronator Teres: Pronates the forearm and assists in flexion.
- Pronator Quadratus: Primary pronator of the forearm.
4. Supinator Muscles
- Supinator: Supinates the forearm.
- Biceps Brachii: Also acts as a supinator when the elbow is flexed.
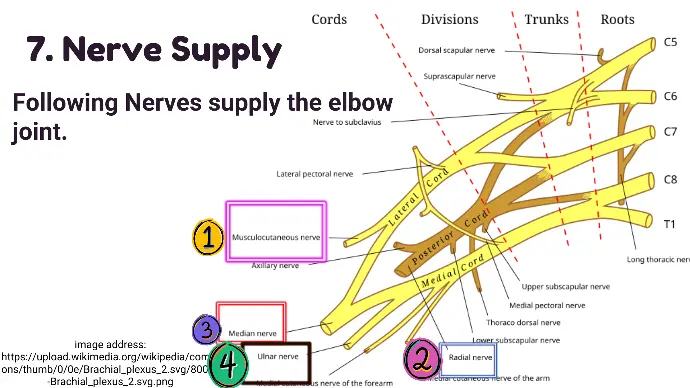
7. Nerve Supply of elbow joint
Following Nerves supply the elbow joint.
- Musculocutaneous Nerve
- Radial Nerve
- Median Nerve
- Ulnar Nerve
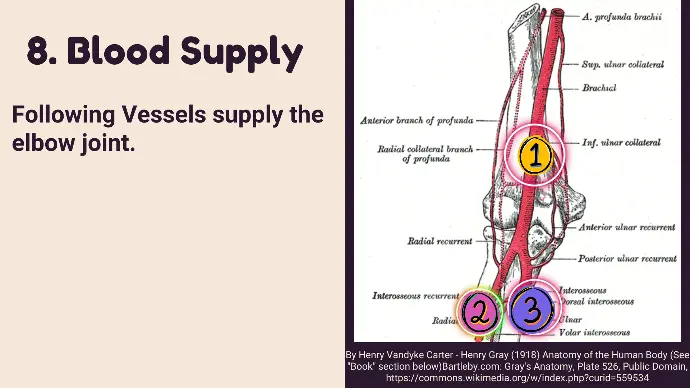
8. Blood Supply of elbow joint
Following Vessels supply the elbow joint.
- Brachial Artery: Major blood supply, continues into the forearm as the radial and ulnar arteries.
- Radial Artery: Supplies the lateral aspect of the forearm.
- Ulnar Artery: Supplies the medial aspect of the forearm.