Anatomy of the Cubital Fossa
The cubital fossa is an anatomical region located on the anterior aspect of the elbow.
As its name says in Latin.
Cubitus meaning "Elbow"

Boundaries of the Cubital Fossa
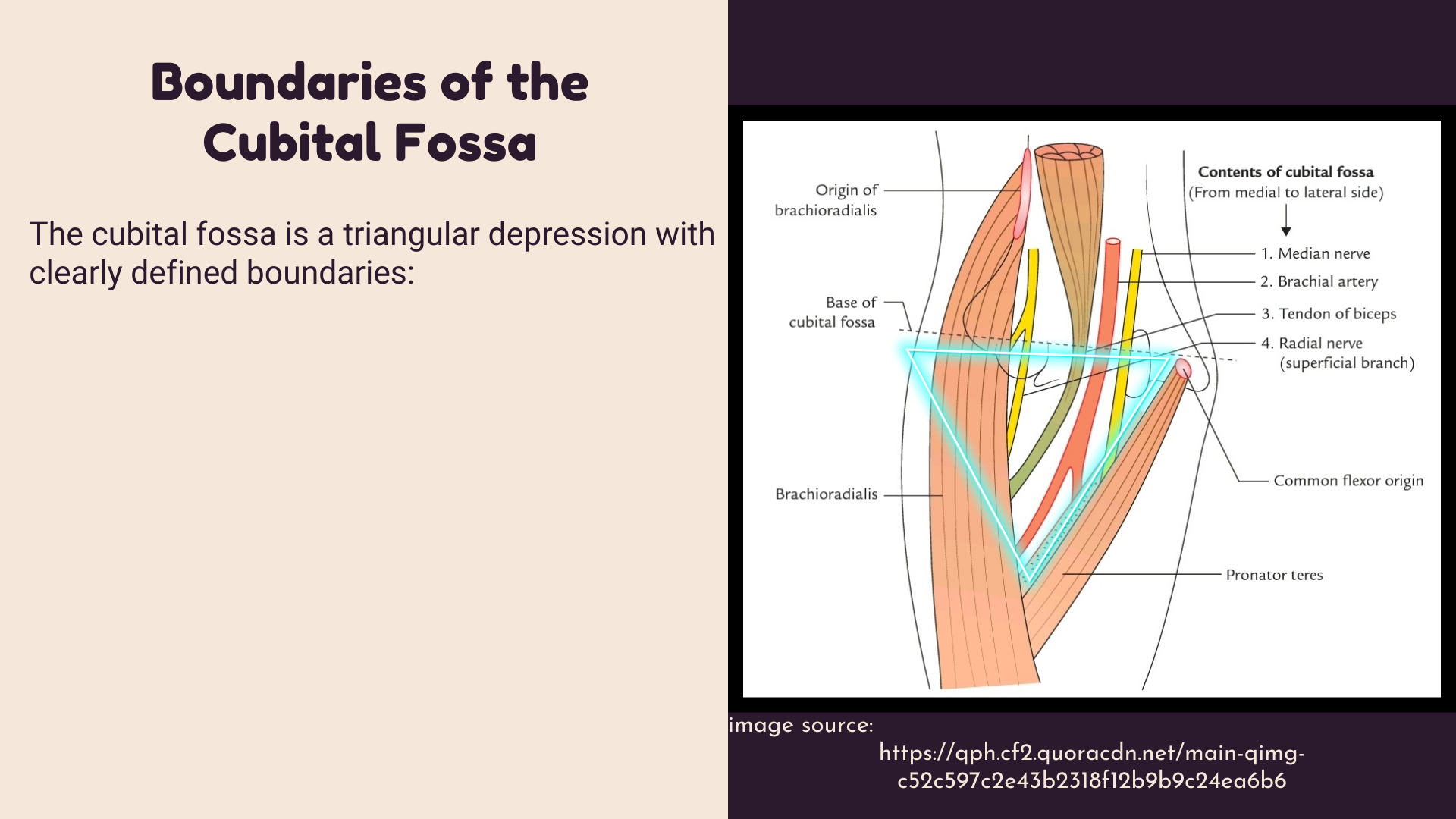
The cubital fossa is a triangular depression with clearly defined boundaries:
- Superior Boundary: An imaginary line connecting the medial and lateral epicondyles of the humerus.
- Medial Boundary: The lateral border of the pronator teres muscle.
- Lateral Boundary: The medial border of the brachioradialis muscle.
- Apex: it is directed downwards, and it is the point, where brachioradialis crosses pronator teres muscle.
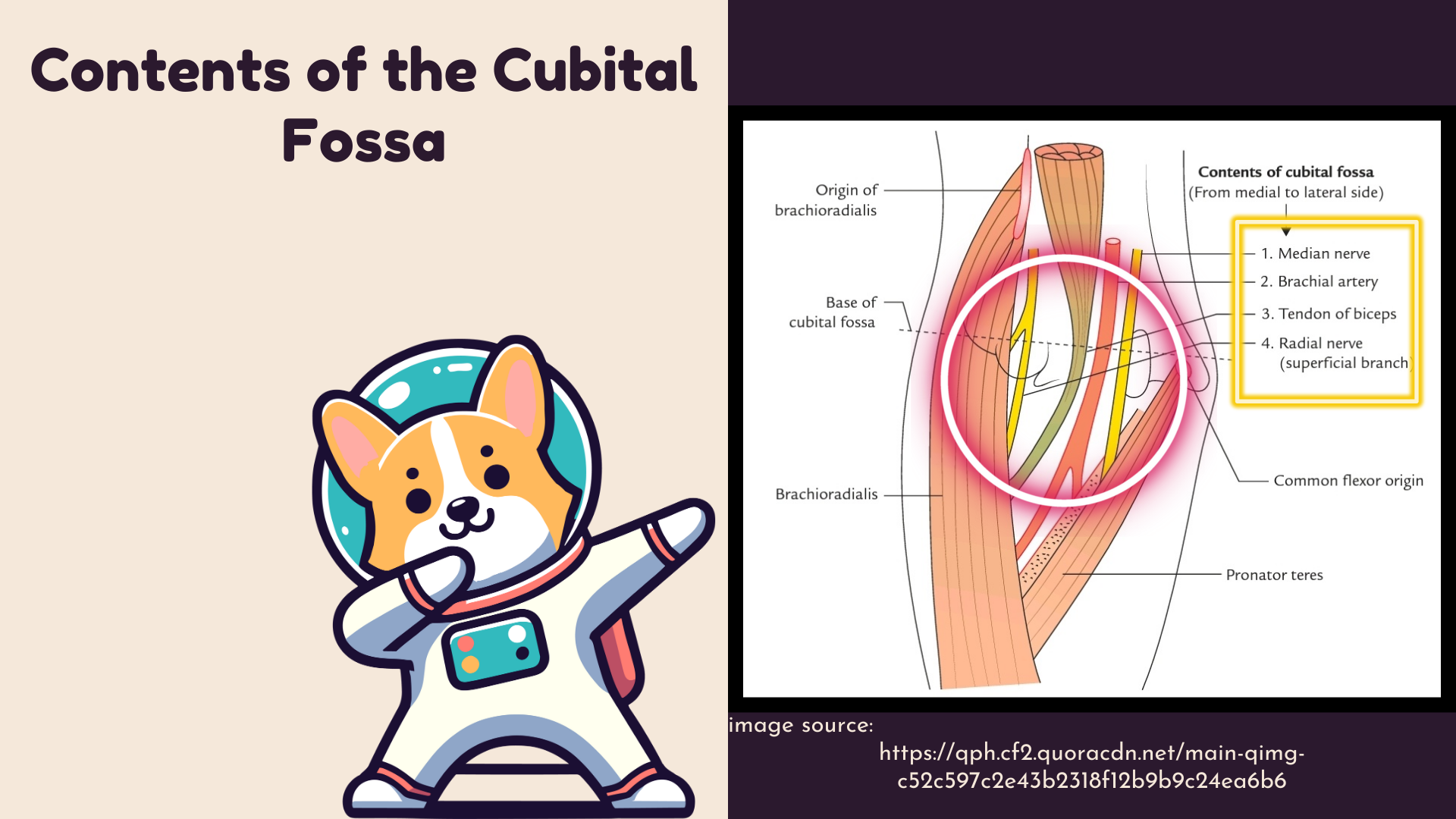
Contents of the Cubital Fossa
The cubital fossa contains several important structures,
Arranged from medial to lateral, its Contents are:
- Median Nerve
- Brachial Artery
- Biceps Brachii Tendon
- Radial Nerve
It is also remembered by the mnemonic:
MBBR
Detailed Anatomy of Key Structures
1. Median Nerve
- Origin: Formed by the union of the lateral and medial cords of the brachial plexus.
- Course: Descends through the arm, passing through the cubital fossa, and enters the forearm.
2. Brachial Artery
- Origin: Continuation of the axillary artery.
- Course: Travels down the arm, enters the cubital fossa, and divides into the radial and ulnar arteries.
3. Biceps Brachii Tendon
- Origin: Biceps brachii muscle.
- Insertion: Radial tuberosity and bicipital aponeurosis.
- Function: Flexes the elbow and supinates the forearm.
4. Radial Nerve
- Origin: Posterior cord of the brachial plexus.
- Course: Travels in the radial groove of the humerus, crosses the elbow anteriorly, and divides into superficial and deep branches.