Introduction to Bones:
Bones Tissue Structure and Their Types
Bones are fundamental components of the human skeleton, providing structure, protection, and support for the body. Understanding bone tissue and its types is essential for appreciating their role in human anatomy and health.

What are Bones?
Bones are a specialized form of connective tissue that constitutes most of the human skeleton. In an adult human body, there are 206 bones, each serving unique functions essential for overall bodily function and structure.
Characteristics of Bones:
- Mineralized Tissue: Bones are hard and strong due to their mineral content, primarily composed of calcium, phosphate, and magnesium.
Bone Tissue
Bone tissue, also known as osseous tissue, is the structural framework of bones. It is characterized by:
- Bone Cells: Primarily osteocytes, which are embedded within the bone matrix.
- Intercellular Substance/Matrix: Composed of collagen fibers and ground substance, which provides structural support and strength to the bone.
Bone Minerals
The ground substance of bones is a critical reservoir for the body's minerals.
It stores a significant portion of essential minerals, including:
- 97% of the Body’s Calcium
- 86% of Phosphate
- 54% of Magnesium
Types of Bone Tissue
Human bones are classified into two main types based on their tissue structure: compact bones and spongy bones.
1. Compact Bones
Compact bones are dense and form the outer layer of bone structures. They are known for their hard, solid appearance, with minimal cavities.
Characteristics of Compact Bones:
- Haversian Systems: Also known as osteons, these are cylindrical structures that make up the compact bone. They consist of concentric layers of calcified bone tissue.
- Haversian Canals: Each Haversian system contains a central canal that runs longitudinally. This canal houses blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerves, supplying the bone with essential nutrients and maintaining its health.

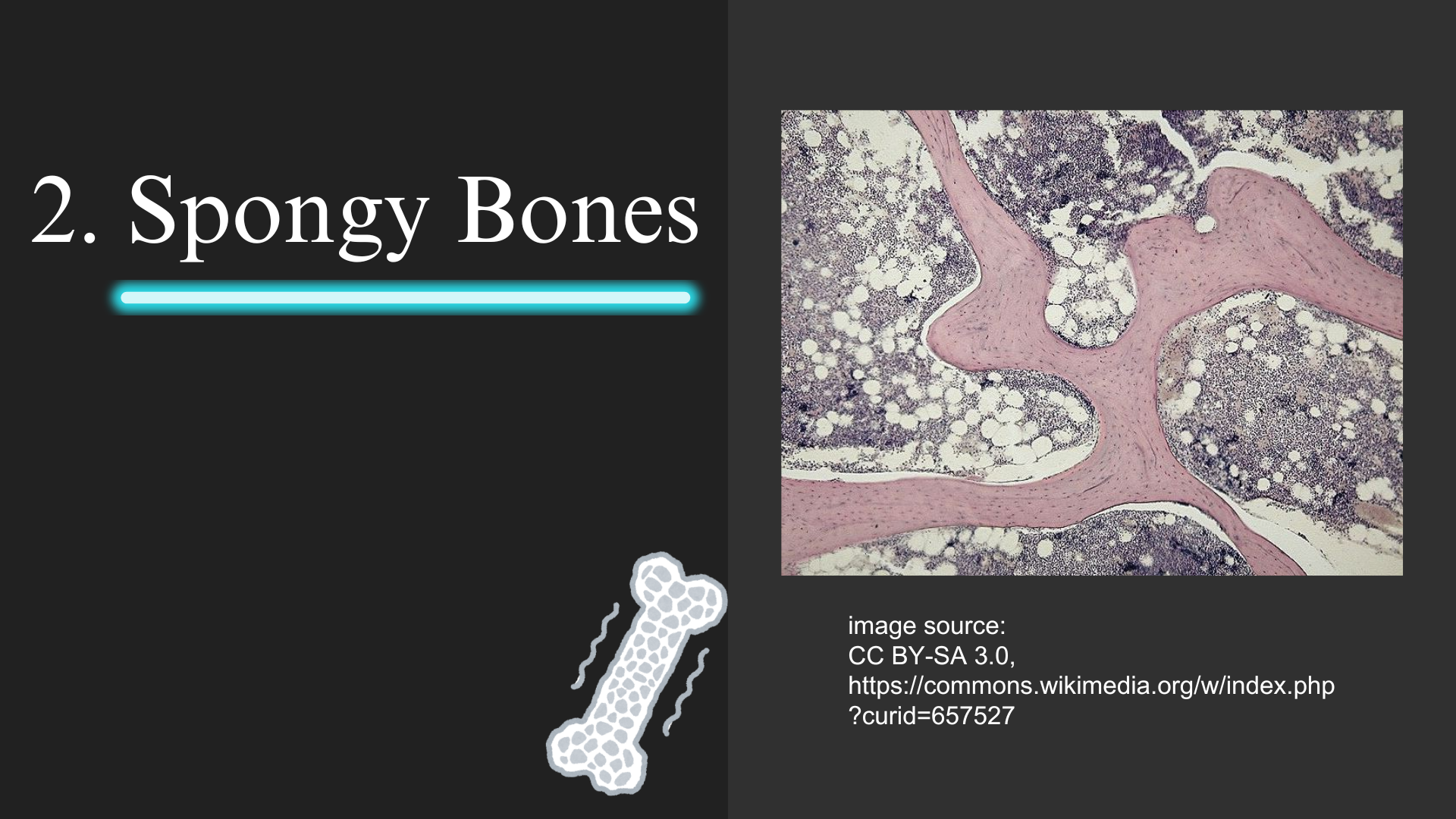
2. Spongy Bones
Spongy bones, or cancellous bones, are found predominantly at the ends of long bones and in the interior of others. They are characterized by a porous, lattice-like structure.
Characteristics of Spongy Bones:
- Structure: Composed of an irregular meshwork of bony trabeculae. The trabeculae are interconnected, forming a network that supports the bone's structure.
- Composition: The trabeculae contain collagen fibers and osteoblasts, which are crucial for bone formation and maintenance.
- Bone Marrow: Red bone marrow is located in the spaces between trabeculae. It is rich in adipocytes (fat cells) and hematopoietic stem cells, which are responsible for producing blood cells.
Conclusion
Bones are complex structures with specialized tissues that provide essential functions for the body. Compact bones offer strength and rigidity, while spongy bones provide flexibility and house vital marrow. Understanding these types of bone tissue helps in appreciating their roles in overall skeletal health and function.