Arteries of the Upper Limb
The primary arteries supplying the upper limb include
- the subclavian artery
- axillary artery
- brachial artery
- radial artery
- ulnar artery
1. Subclavian Artery
Origin: The right subclavian artery originates from the brachiocephalic trunk, while the left subclavian artery arises directly from the aortic arch.
Course: Travels laterally under the clavicle, becoming the axillary artery at the lateral border of the first rib.
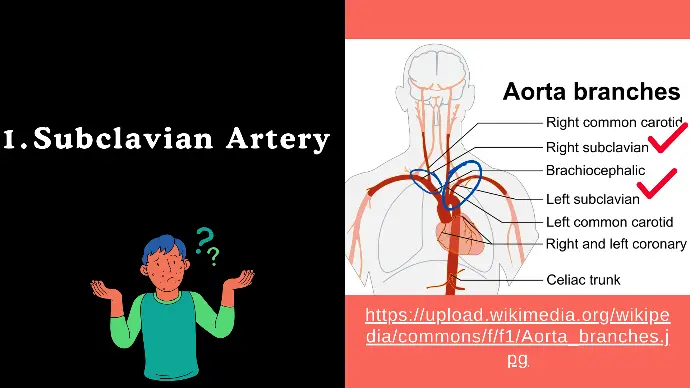
Branches : It gives 4 Branches.
- Vertebral Artery: Supplies the posterior part of the brain.
- Internal Thoracic Artery: Supplies the anterior chest wall and breasts.
- Thyrocervical Trunk: Gives off several branches, including the inferior thyroid artery, transverse cervical artery, and suprascapular artery.
- Costocervical Trunk: Supplies the deep neck muscles and the first two intercostal spaces.
2. Axillary Artery
Origin: Continuation of the subclavian artery at the lateral border of the first rib.
Course: Travels through the axilla, becoming the brachial artery at the inferior border of the teres major muscle.
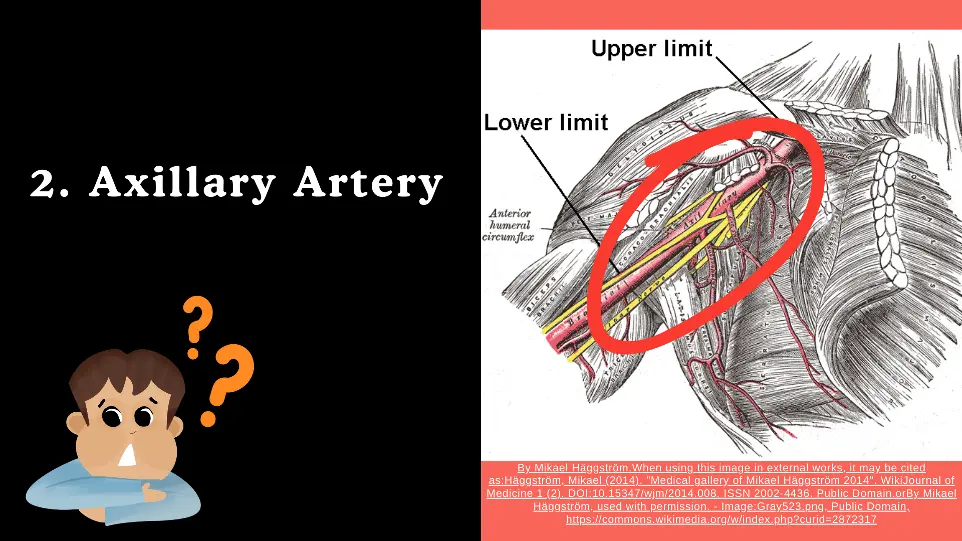
Divisions :
Division into Three Parts
The axillary artery is divided into three parts based on its position relative to the pectoralis minor muscle.
- First Part (proximal to muscle).
- Second part (deep to muscle).
- Third Part (distal to muscle).
3. Brachial Artery
Origin: Continuation of the axillary artery at the inferior border of the teres major muscle.
Course: Travels down the medial aspect of the arm, entering the cubital fossa at the elbow.
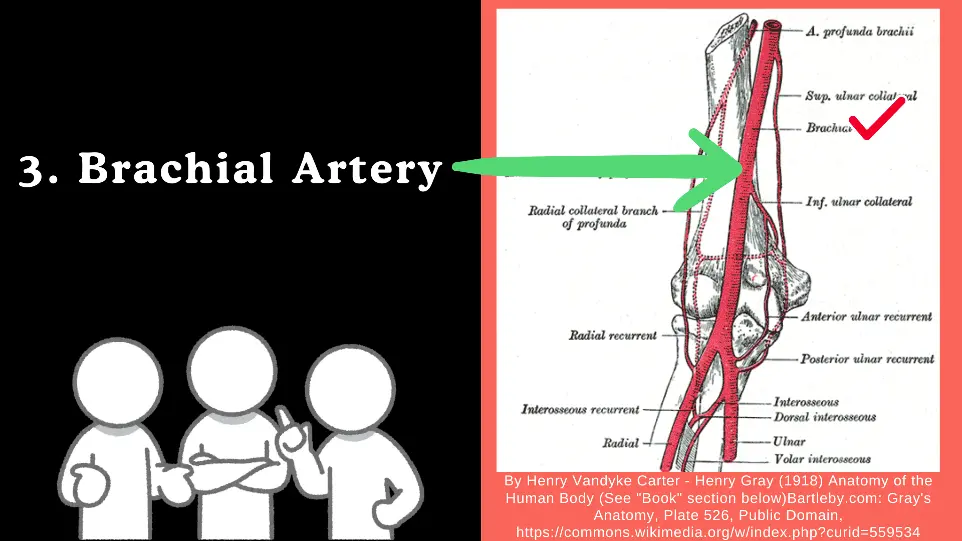
Branches:
Brachial Artery gives following Four Branches.
- Profunda Brachii (Deep Brachial Artery): Supplies the posterior compartment of the arm.
- Nutrient Artery to the Humerus: Supplies the humerus.
- Superior Ulnar Collateral Artery: Runs with the ulnar nerve, supplies the elbow joint.
- Inferior Ulnar Collateral Artery: Supplies the elbow joint.
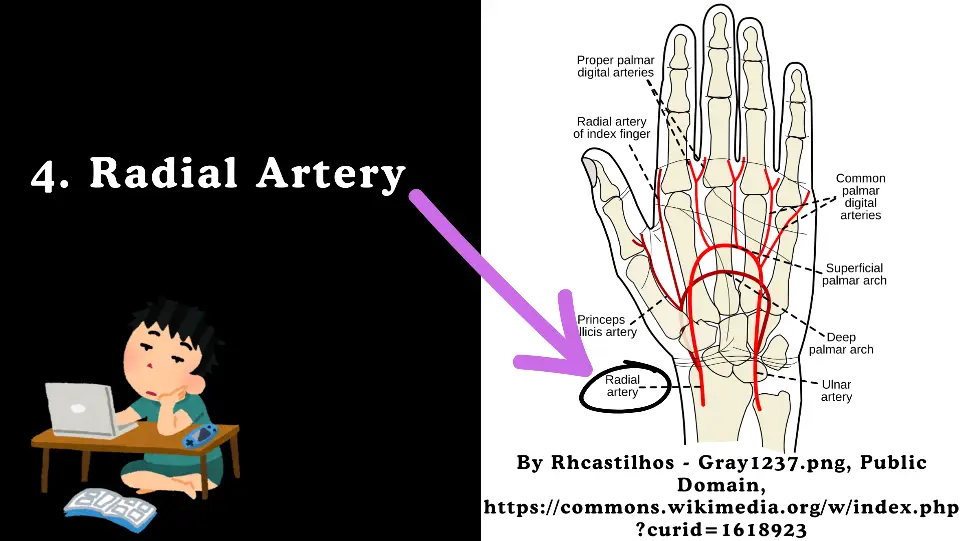
4. Radial Artery
Origin: Begins at the bifurcation of the brachial artery in the cubital fossa.
Course: Travels down the lateral aspect of the forearm, passes through the anatomical snuffbox, and enters the hand.
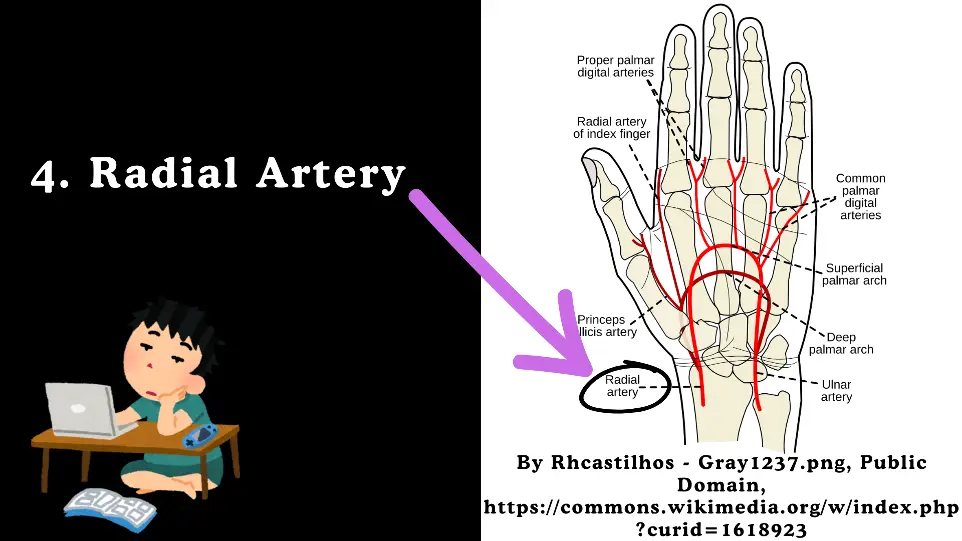
Branches :
Radial Artery gives following four Branches.
- Radial Recurrent Artery: Supplies the elbow joint.
- Palmar Carpal Branch: Supplies the carpal bones and joints.
- Superficial Palmar Branch: Contributes to the superficial palmar arch.
- Deep Palmar Arch: Supplies the deep structures of the hand.
5. Ulnar Artery
Origin: Begins at the bifurcation of the brachial artery in the cubital fossa.
Course: Travels down the medial aspect of the forearm, enters the hand via the Guyon canal.
Branches :
Ulnar Artery gives following five Branches.
- Ulnar Recurrent Arteries (Anterior and Posterior): Supply the elbow joint.
- Common Interosseous Artery: Divides into anterior and posterior interosseous arteries, supplying the forearm.
- Palmar Carpal Branch: Supplies the carpal bones and joints.
- Superficial Palmar Arch: Supplies the superficial structures of the hand.
- Deep Palmar Branch: Contributes to the deep palmar arch.